Searching is integral to life - We search for things all the time; or at least I do! As often is the case, just as it is in life, so it is in computer science and searching plays a very important role when it comes to working with data. A search algorithm is any algorithm which solves the Search problem, namely, to retrieve information stored within some data structure, or calculated in the search space of a problem domain. Examples of such structures include but are not limited to a Linked List, an Array data structure, or a Search tree. The appropriate search algorithm often depends on the data structure being searched, but also on any a priori knowledge about the data. Searching also encompasses algorithms that query the data structure, such as the SQL SELECT command.
Linear Search Algorithm
The _Linear Search a_lgorithm is a simple algorithm, where each item in the list (starting from the first item) is investigated until the required item is found, or the end of the list is reached.
The Linear Search algorithm is implemented in Python as follows:
def linearSearch(item, my_list):
found = False
position = 0
while position < len(my_list) and not found:
if my_list[position] == item:
found = True
position = position + 1
return found
Let's test the code. Enter the following statement at the end of the Python script above:
bag = ['book', 'pencil', 'pen', 'note book', 'sharpener', 'eraser']
item = input('What item do you want to check for in the bag?')
itemFound = linearSearch(item, bag)
if itemFound:
print ('Yes, the item is in the bag')
else:
print ('Oops, your item seems not to be in the bag')
When you enter the input, make sure it is between single or double quotes (i.e. 'pencil'). If you input 'pencil', for instance, you should get the following output:
Yes, the item is in the bag
Whereas, if you enter 'ruler' as input, you will get the following output:
Oops, your item seems not to be in the bag
As we can see, Python proves itself again to be a programming language that makes it easy to program algorithmic concepts as we did here, dealing with sorting and searching algorithms.
It is important to note that there are other types of sorting and searching algorithms.
Binary Search
Given a sorted array arr[] of n elements, write a function to search a given element x in arr[].
A simple approach is to do linear search . The time complexity of above algorithm is O(n). Another approach to perform the same task is using Binary Search.
Binary Search: Search a sorted array by repeatedly dividing the search interval in half. Begin with an interval covering the whole array. If the value of the search key is less than the item in the middle of the interval, narrow the interval to the lower half. Otherwise narrow it to the upper half. Repeatedly check until the value is found or the interval is empty.
Binary Search
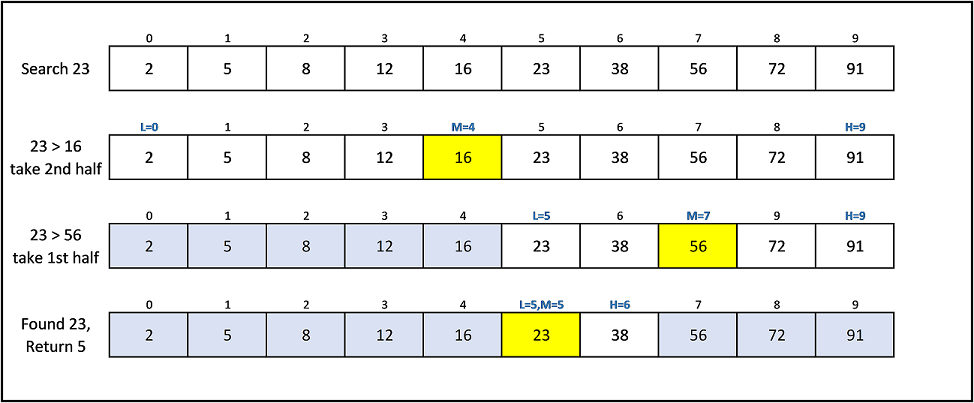
The idea of binary search is to use the information that the array is sorted and reduce the time complexity to O(Log n).
We basically ignore half of the elements just after one comparison.
- Compare x with the middle element.
- If x matches with middle element, we return the mid index.
- Else If x is greater than the mid element, then x can only lie in right half subarray after the mid element. So we recur for right half.
- Else (x is smaller) recur for the left half.