Performance Lab Set #1
Task 1
- Use the following Tree to answer the six questions.
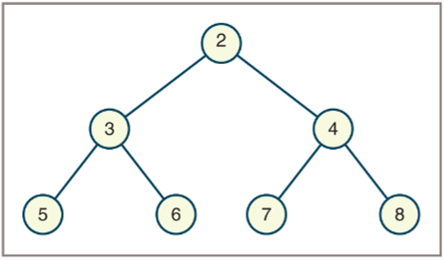
- What are the leaf nodes in the tree?
- What are the interior nodes in the tree?
- What are the siblings of node 7?
- What is the height of the tree?
- How many nodes are in level 2?
- Is the tree a general tree, a binary tree, or both?
Task 2
- What is the difference between a perfectly balanced binary tree and a complete binary tree?
- What is the difference between a complete binary tree and a full binary tree?
- A full binary tree has a height of 5. How many nodes does it contain?
- A complete binary tree contains 125 nodes. What is its height?
- How many nodes are on a given level L in a full binary tree? Express your answer in terms ofL.
Task 3
- What is the heap property for a min-heap?
- How is a binary search tree different from a binary tree?
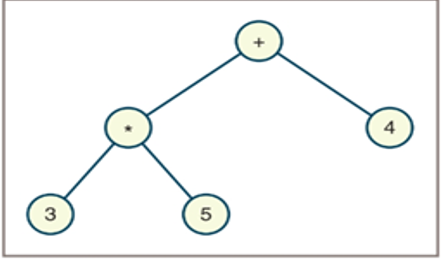
- Write the expression represented by the following expression tree in infix, prefix, and postfix notations.(Hint: Use the inorder, preorder, and postorder traversals described in this section to obtain your answers.)
- Draw diagrams of the expression trees for the following expressions: a. 35 + 6 b. 3 + 56 c. 356
Task 4
- Describe how insertions can have a negative effect on subsequent searches of a binary search tree.
- Discuss the trade-offs between the array-based implementation of a sorted bag presented in Chapter 6 and a binary search tree implementation of a sorted bag.
Task 5
- Assume that a node is at position 12 in an array representation of a binary tree. Give the positions of that node's parent, left child, and right child.
- Whar are the constraints on a binary tree that is contained in an array?
Task 6
- How do the run times of the heap operation differ from their counterparts in binary search trees?
- What is the advantage of using a list over using an array to implement a heap?
- The heap sort uses a heap to sort a list of items. The strategy of this sort is to add the items in the list to a heap and then remove all of them from the heap as they are transferred back to the list. What is the run time and memory complexity of the heap sort?
Performance Lab Set #2
- Write a Python program to create a Balanced Binary Search Tree (BST) using an array (given) elements where array elements are sorted in ascending order.
- Write a Python program to find the closest value of a given target value in a given non-empty Binary Search Tree (BST) of unique values.
- Write a Python program to check whether a given a binary tree is a valid binary search tree (BST) or not.
Let a binary search tree (BST) is defined as follows: The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys less than the node's key. The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys greater than the node's key. Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
Example 1:
2
/ \
1 3
Binary tree [2,1,3], return true.
Example 2:
1
/ \
2 3
Binary tree [1,2,3], return false.
-
Write a Python program to delete a node with the given key in a given Binary search tree (BST).
Note: Search for a node to remove. If the node is found, delete the node. -
Write a Python program to convert a given array elements to a height balanced Binary Search Tree (BST).
-
Write a Python program to find the kth smallest element in a given a binary search tree.
Submit your assignment